What Two Organelles Can Be Found In Plant Cells But Not Animal
Learning Outcomes
- Identify central organelles present merely in animal cells, including centrosomes and lysosomes
- Place key organelles present only in institute cells, including chloroplasts and big central vacuoles
At this indicate, yous know that each eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, a nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, and in some, vacuoles, simply there are some hitting differences between animal and constitute cells. While both beast and plant cells have microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), animate being cells likewise have centrioles associated with the MTOC: a complex called the centrosome. Animal cells each have a centrosome and lysosomes, whereas plant cells do not. Constitute cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts and other specialized plastids, and a large central vacuole, whereas animate being cells do not.
Properties of Fauna Cells

Effigy 1. The centrosome consists of 2 centrioles that prevarication at right angles to each other. Each centriole is a cylinder made up of 9 triplets of microtubules. Nontubulin proteins (indicated past the green lines) agree the microtubule triplets together.
Centrosome
The centrosome is a microtubule-organizing middle found near the nuclei of animal cells. It contains a pair of centrioles, two structures that lie perpendicular to each other (Figure 1). Each centriole is a cylinder of nine triplets of microtubules.
The centrosome (the organelle where all microtubules originate) replicates itself before a cell divides, and the centrioles appear to have some role in pulling the duplicated chromosomes to contrary ends of the dividing prison cell. However, the verbal function of the centrioles in cell sectionalization isn't clear, because cells that have had the centrosome removed tin can still dissever, and plant cells, which lack centrosomes, are capable of cell division.
Lysosomes

Figure two. A macrophage has engulfed (phagocytized) a potentially pathogenic bacterium and and so fuses with a lysosomes within the prison cell to destroy the pathogen. Other organelles are present in the cell but for simplicity are not shown.
In addition to their role equally the digestive component and organelle-recycling facility of animal cells, lysosomes are considered to be parts of the endomembrane organization.
Lysosomes also utilise their hydrolytic enzymes to destroy pathogens (disease-causing organisms) that might enter the prison cell. A good case of this occurs in a group of white blood cells chosen macrophages, which are part of your body's immune arrangement. In a procedure known as phagocytosis or endocytosis, a department of the plasma membrane of the macrophage invaginates (folds in) and engulfs a pathogen. The invaginated department, with the pathogen inside, then pinches itself off from the plasma membrane and becomes a vesicle. The vesicle fuses with a lysosome. The lysosome's hydrolytic enzymes then destroy the pathogen (Effigy two).
Properties of Plant Cells
Chloroplasts
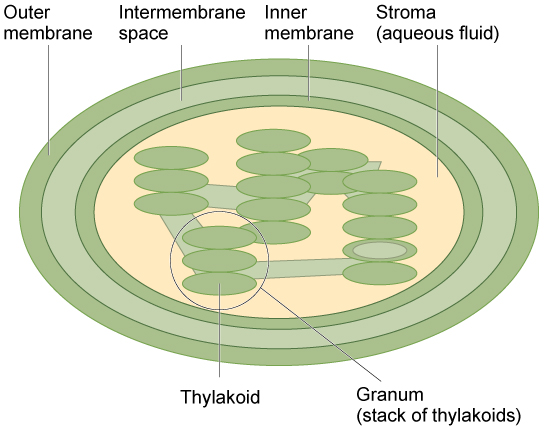
Figure 3. The chloroplast has an outer membrane, an inner membrane, and membrane structures called thylakoids that are stacked into grana. The space inside the thylakoid membranes is called the thylakoid space. The light harvesting reactions have place in the thylakoid membranes, and the synthesis of sugar takes identify in the fluid inside the inner membrane, which is chosen the stroma. Chloroplasts also have their own genome, which is contained on a unmarried circular chromosome.
Like the mitochondria, chloroplasts accept their own Dna and ribosomes (we'll talk near these afterward!), but chloroplasts have an entirely different function. Chloroplasts are plant cell organelles that carry out photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the series of reactions that use carbon dioxide, water, and lite energy to brand glucose and oxygen. This is a major difference between plants and animals; plants (autotrophs) are able to make their own food, similar sugars, while animals (heterotrophs) must ingest their food.
Similar mitochondria, chloroplasts have outer and inner membranes, but inside the space enclosed by a chloroplast's inner membrane is a set of interconnected and stacked fluid-filled membrane sacs chosen thylakoids (Effigy three). Each stack of thylakoids is called a granum (plural = grana). The fluid enclosed past the inner membrane that surrounds the grana is called the stroma.
The chloroplasts contain a dark-green pigment called chlorophyll, which captures the light free energy that drives the reactions of photosynthesis. Like establish cells, photosynthetic protists also have chloroplasts. Some leaner perform photosynthesis, but their chlorophyll is not relegated to an organelle.
Try It
Click through this activity to acquire more than nearly chloroplasts and how they work.
Endosymbiosis
Nosotros have mentioned that both mitochondria and chloroplasts contain DNA and ribosomes. Have you wondered why? Strong evidence points to endosymbiosis as the explanation.
Symbiosis is a relationship in which organisms from 2 split up species depend on each other for their survival. Endosymbiosis (endo– = "inside") is a mutually benign relationship in which i organism lives within the other. Endosymbiotic relationships abound in nature. We have already mentioned that microbes that produce vitamin Thousand live inside the human gut. This human relationship is beneficial for us considering nosotros are unable to synthesize vitamin K. It is too beneficial for the microbes because they are protected from other organisms and from drying out, and they receive abundant food from the environment of the large intestine.
Scientists have long noticed that bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are like in size. We also know that bacteria have DNA and ribosomes, just as mitochondria and chloroplasts do. Scientists believe that host cells and bacteria formed an endosymbiotic human relationship when the host cells ingested both aerobic and autotrophic leaner (blue-green alga) but did not destroy them. Through many millions of years of development, these ingested leaner became more than specialized in their functions, with the aerobic bacteria condign mitochondria and the autotrophic leaner condign chloroplasts.
Figure four. The Endosymbiotic Theory. The starting time eukaryote may have originated from an ancestral prokaryote that had undergone membrane proliferation, compartmentalization of cellular office (into a nucleus, lysosomes, and an endoplasmic reticulum), and the establishment of endosymbiotic relationships with an aerobic prokaryote, and, in some cases, a photosynthetic prokaryote, to grade mitochondria and chloroplasts, respectively.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that part in storage and transport. The membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. Additionally, some agents such as enzymes within plant vacuoles suspension down macromolecules.
If you lot look at Effigy 5b, you will see that plant cells each have a large fundamental vacuole that occupies virtually of the area of the jail cell. The central vacuole plays a fundamental function in regulating the cell's concentration of water in changing environmental conditions. Take you ever noticed that if you lot forget to h2o a plant for a few days, information technology wilts? That's because equally the water concentration in the soil becomes lower than the h2o concentration in the plant, water moves out of the cardinal vacuoles and cytoplasm. Every bit the central vacuole shrinks, it leaves the cell wall unsupported. This loss of back up to the cell walls of plant cells results in the wilted advent of the plant.
The fundamental vacuole also supports the expansion of the cell. When the key vacuole holds more water, the cell gets larger without having to invest a lot of energy in synthesizing new cytoplasm. You can rescue wilted celery in your refrigerator using this process. Simply cut the end off the stalks and place them in a cup of h2o. Soon the celery will exist potent and crunchy once again.

Figure 5. These figures show the major organelles and other jail cell components of (a) a typical animal prison cell and (b) a typical eukaryotic plant cell. The plant jail cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, plastids, and a central vacuole—structures not found in animal cells. Plant cells practise not accept lysosomes or centrosomes.
Effort It
Contribute!
Did yous accept an idea for improving this content? Nosotros'd love your input.
Improve this pageLearn More
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-biology1/chapter/reading-unique-features-of-plant-cells/
Posted by: tathamferamplon.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Two Organelles Can Be Found In Plant Cells But Not Animal"
Post a Comment